
Conceptual design is the initial phase of the product development process, where innovative ideas are transformed into detailed design concepts. It focuses on defining the functionality, appearance, and overall structure of the product. During this stage, designers explore various creative solutions and identify the best approach to meet client needs and project goals.
The process involves sketching, 3D modeling, and simulations to visualize how the product will function. Conceptual design helps in aligning the design vision with practical requirements, ensuring that the final product is both functional and aesthetically appealing.
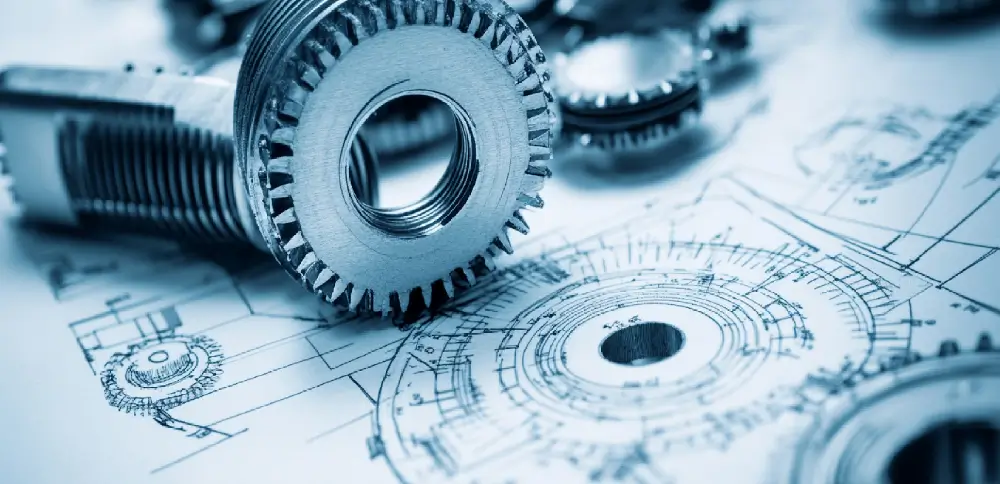
General assembly drawings are comprehensive illustrations that provide an overall view of how different parts of a product fit and work together. These drawings include detailed depictions of all components, their positions, and how they are assembled into a complete product.
Typically used by engineers and manufacturers, they help ensure that every part is correctly aligned and assembled according to the design specifications. These drawings often include part numbers, material details, and assembly instructions, making them essential for both production and quality control.
Fabrication drawings are detailed technical documents that provide all the necessary information for manufacturing individual components of a product. These drawings include precise dimensions, materials, tolerances, and instructions for processes such as cutting, welding, or machining, ensuring that each part is made to the exact specifications required for assembly.
They often include detailed views of complex components, material specifications, and special notes related to finishing or treatment. Fabrication drawings are critical in industries like construction, engineering, and manufacturing, as they ensure accuracy, consistency, and quality in the production process.
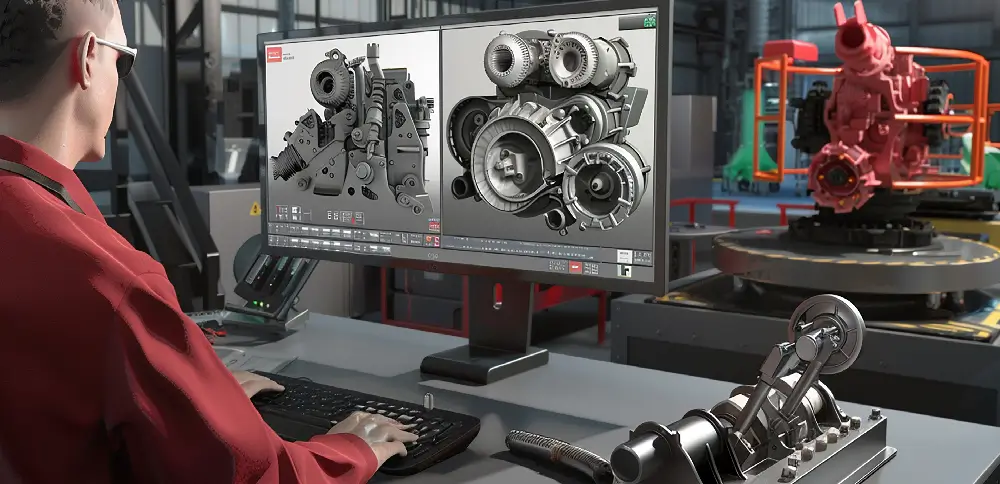
Product design is the process of developing functional and aesthetically appealing products that meet the needs of consumers. It involves conceptualizing ideas, creating prototypes, and refining designs based on usability, performance, and customer feedback.
In product design, designers balance creativity and technical feasibility to ensure the final product is both innovative and manufacturable. This process also includes selecting appropriate materials, optimizing manufacturing processes, and ensuring the design aligns with brand identity and market trends.

2D drawings provide flat, detailed representations of an object, often including dimensions, materials, and annotations necessary for manufacturing. These are typically used for technical documentation and blueprints.
3D drawings or models, on the other hand, offer a more realistic, spatial view, allowing designers and engineers to visualize the product from multiple angles. 3D modeling enables simulations, prototyping, and design optimizations, giving a more comprehensive understanding of how a product will function and appear in the real world.
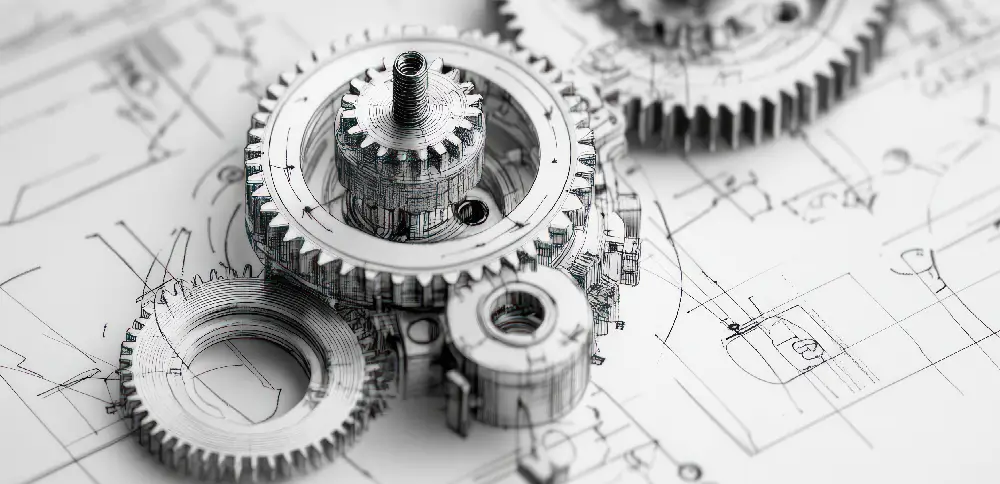
Manufacturing drawings are essential technical documents used to convey the specifications and details of mechanical components and assemblies. These drawings provide critical information such as dimensions, tolerances, material specifications, and surface finishes, ensuring that manufacturers can accurately produce the intended parts.
They typically include multiple views—such as front, top, and side elevations—along with sectional views to illustrate internal features. Clear annotations and symbols are used to communicate manufacturing processes, assembly instructions, and inspection criteria.

